
Opinion | Georgia’s regime has given critics a choice: prison or exile
A new draconian legislative package that vaguely defines a ‘foreign grant’ is placing anyone tangentially related to politics at risk of imprisonment.
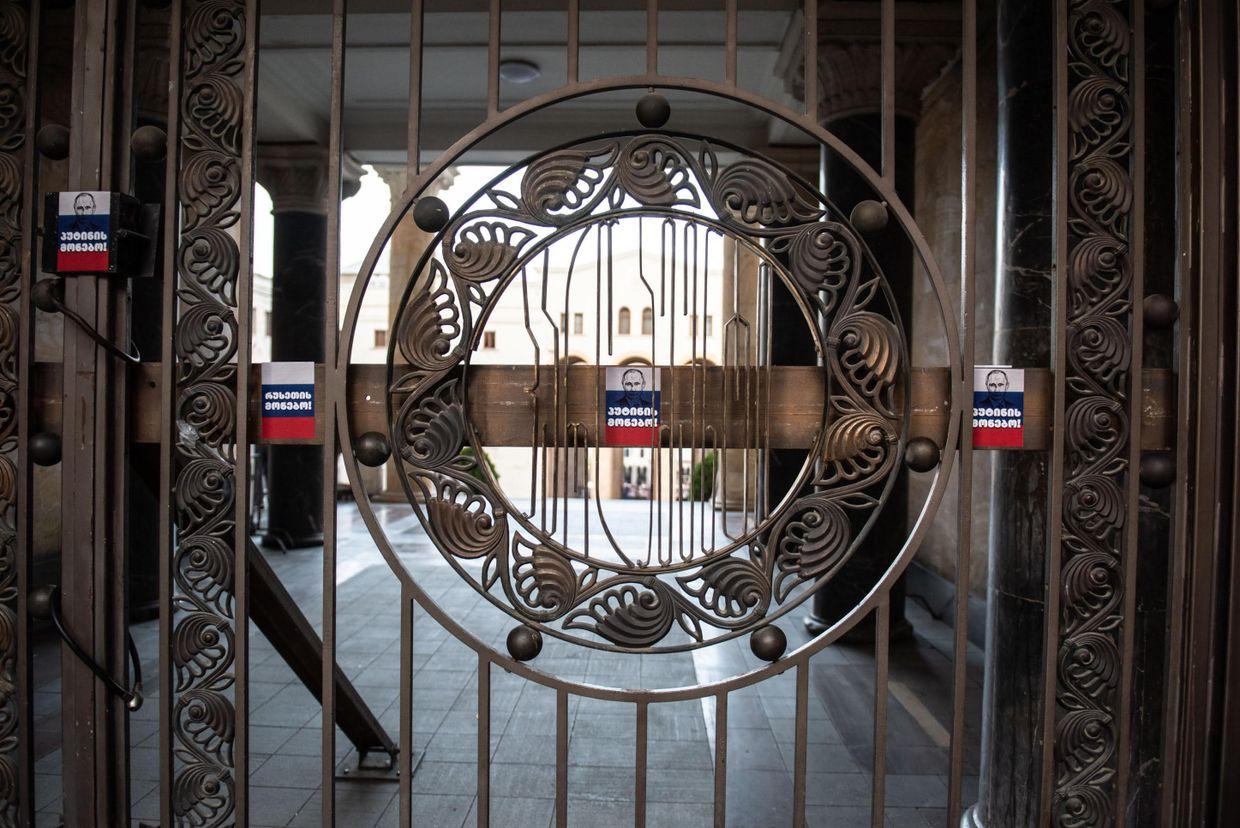

The foreign agent law, dubbed the ‘Russian Law’, labels civil society or media organisations receiving funding from abroad ‘organisations carrying out the interests of a foreign power’. Such organisations are subject to monitoring every six months, which lawyers have warned could include forcing them to hand over internal communications and confidential sources.

A new draconian legislative package that vaguely defines a ‘foreign grant’ is placing anyone tangentially related to politics at risk of imprisonment.
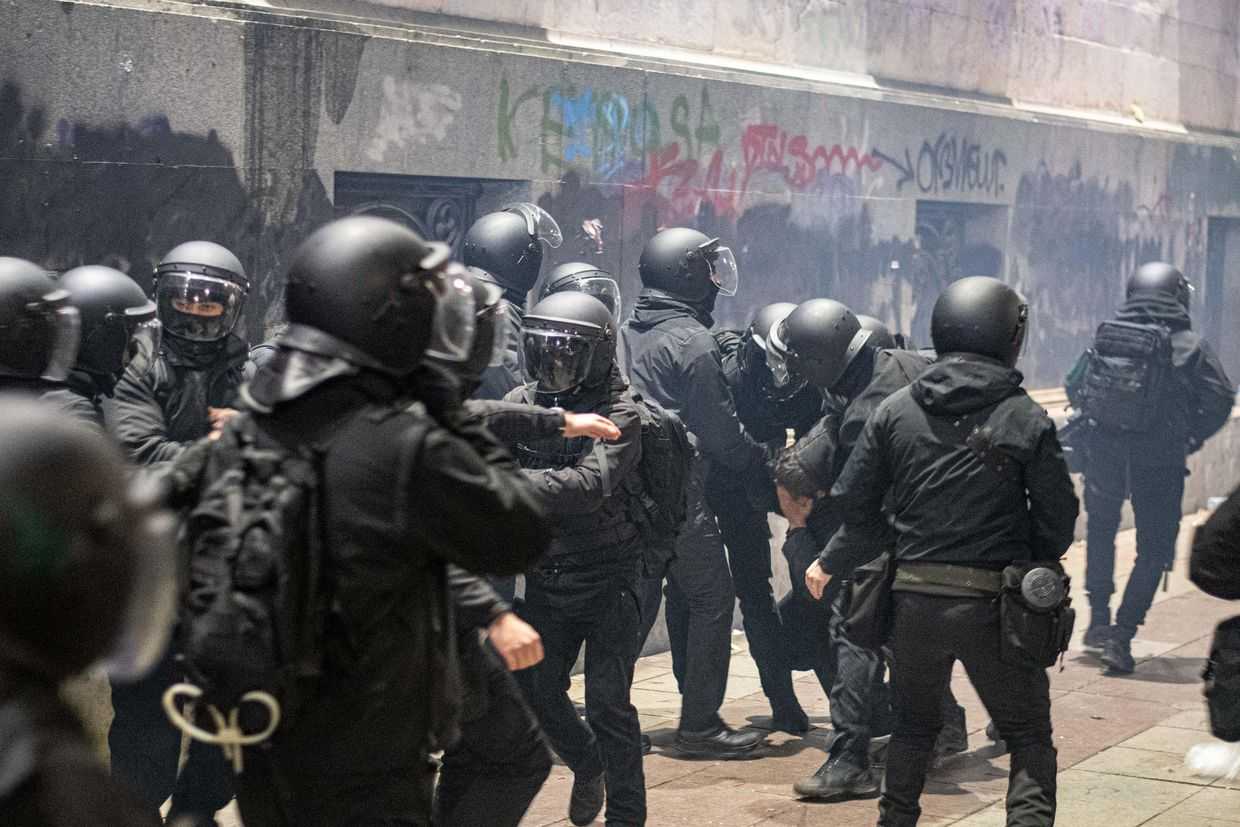

The sheer number of laws passed in recent months have overwhelmed observers and media outlets alike.
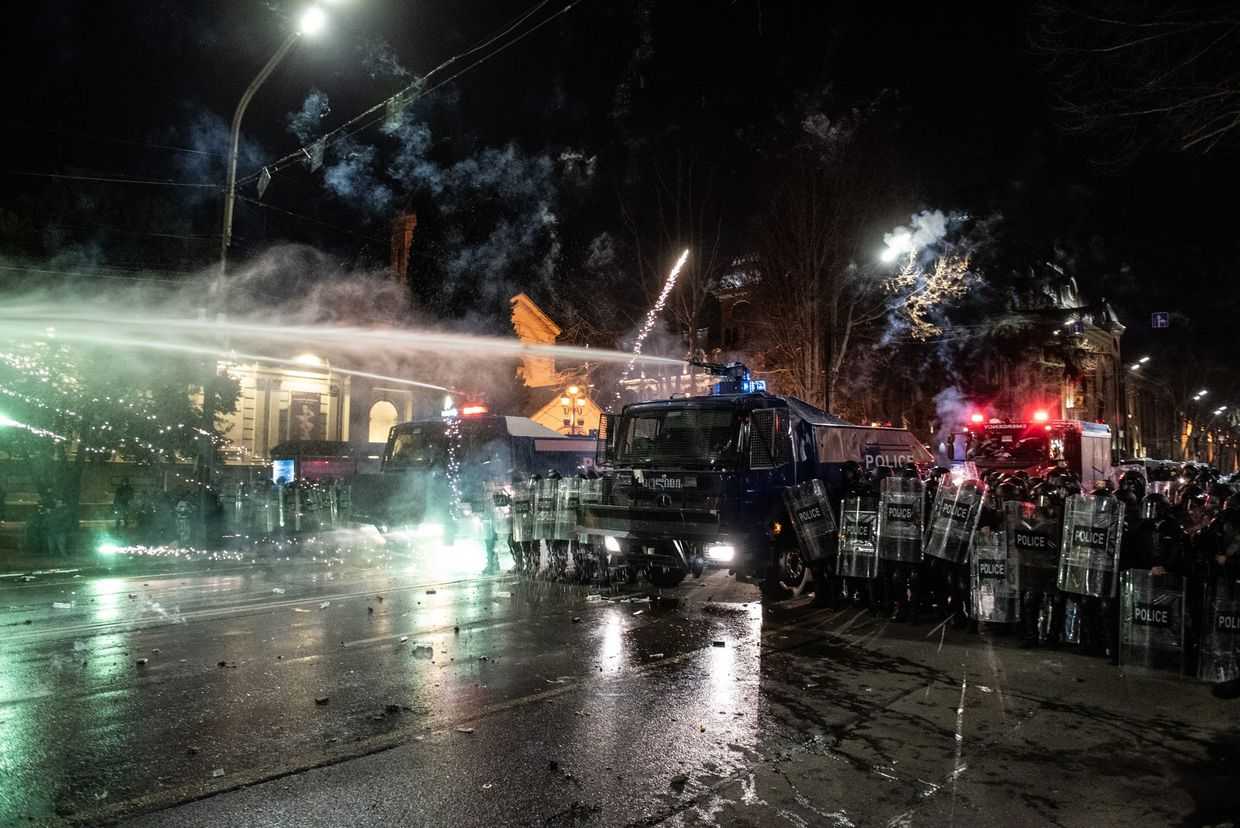
The 19 journalists were injured by police officers during the 2023 foreign agent law protests.
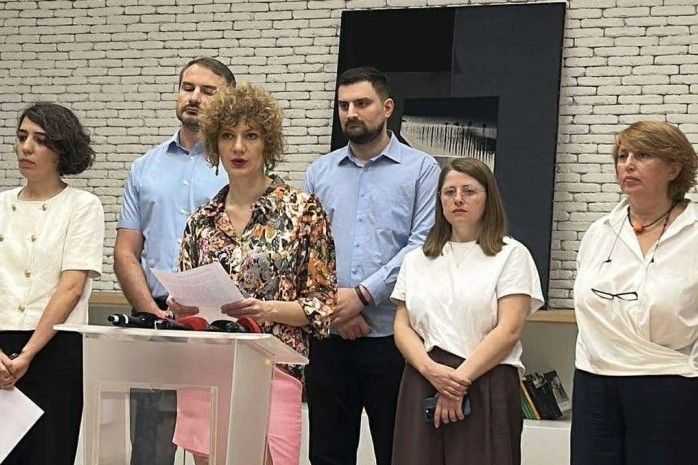

Critics have repeatedly described the ‘Georgian version of FARA’ as a tool of repression.

Georgian Dream supporters are increasingly likely to distrust NGOs while those who trust the opposition have become more trusting.

An ephemeral time capsule of the early foreign agent law protests showing intimate portraits of the young Georgians caught in their midst.
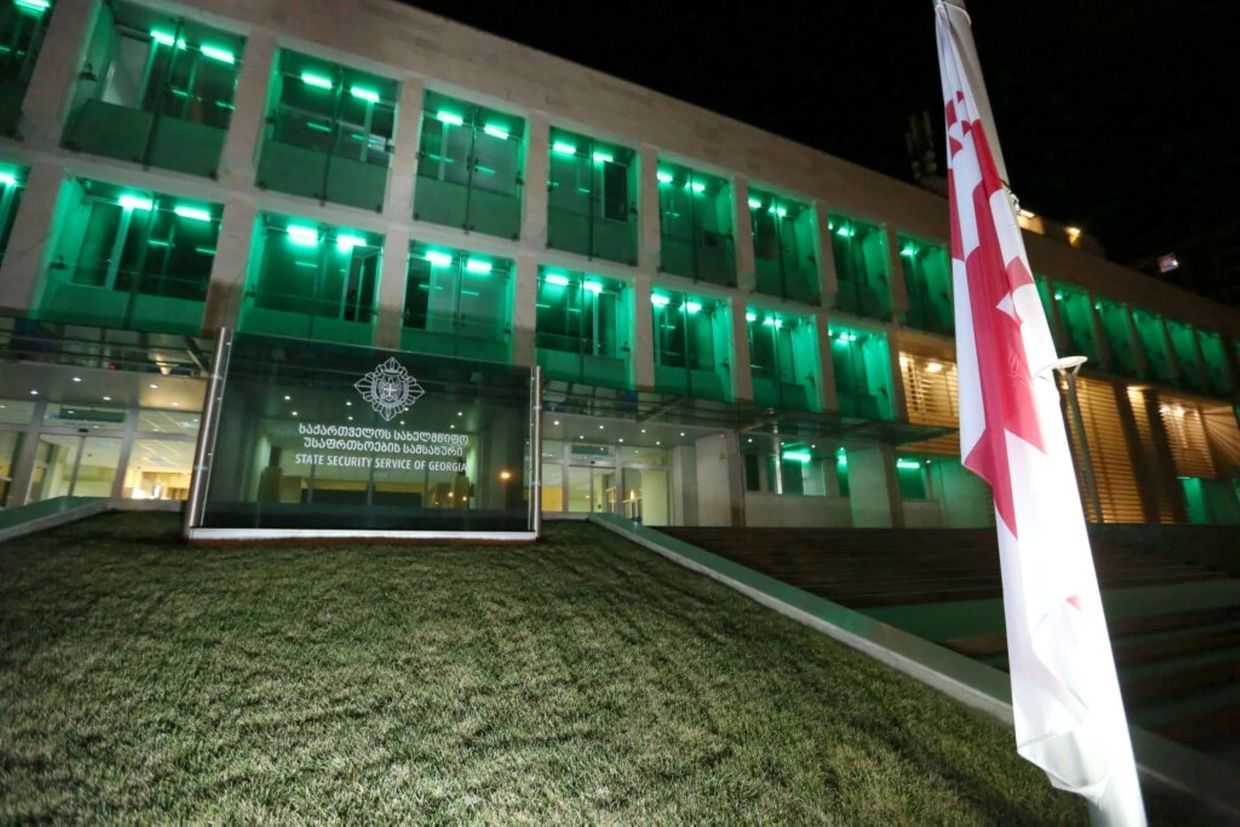

Georgian Dream has repeatedly accused domestic and outside forces of plotting a coup.